How Many Light Years Is Earth From Mars? A Fascinating Journey Through Space
Hey there, space enthusiasts! Let's dive right into the cosmic mystery of how many light years is Earth from Mars. It's a question that often pops up in conversations about space exploration. So, buckle up because we’re about to embark on an interplanetary adventure filled with fascinating facts and mind-blowing science. Are you ready to explore the mysteries of the universe? Let’s go!
When we think about Mars, our neighboring red planet, it’s easy to get caught up in the awe-inspiring wonder of space. But just how far is Mars from Earth? The answer isn’t as straightforward as you might think. Distances in space can be tricky, especially when we start talking about light years. So, let’s break it down and make it as simple as possible.
Whether you're a budding astronomer or just someone who loves gazing at the stars, understanding the distance between Earth and Mars is key to appreciating the vastness of our solar system. This article will take you through everything you need to know, from the basics of light years to the actual distance between these two planets. Stick around!
What Exactly Are Light Years?
Alright, let’s start with the basics. What the heck is a light year, anyway? Simply put, a light year is the distance that light can travel in one Earth year. Light moves at a blazing speed of about 299,792 kilometers per second (or roughly 186,282 miles per second). When you multiply that by the number of seconds in a year, you get a distance of around 9.46 trillion kilometers (about 5.88 trillion miles). Mind = blown, right?
Now, here’s the kicker: while light years are super useful for measuring vast distances in space, they’re not the best unit when talking about planets within our own solar system. For that, we usually stick to astronomical units (AU) or kilometers/miles. But don’t worry—we’ll cover all the details!
Why Do We Use Light Years?
Light years are essential when discussing distances beyond our solar system. For example, the nearest star to Earth (Proxima Centauri) is about 4.24 light years away. Using kilometers or miles would result in ridiculously large numbers that are hard to grasp. Light years help simplify these massive distances, making it easier for scientists and space enthusiasts alike to communicate about the cosmos.
But when it comes to Earth and Mars, we’re dealing with much smaller distances compared to the vastness of interstellar space. That’s why we don’t usually measure their separation in light years. Still, understanding light years gives us a better appreciation of just how far apart things are in the universe.
How Far is Mars from Earth?
So, how far is Mars from Earth, really? Well, the distance varies depending on where the two planets are in their respective orbits around the Sun. On average, Mars is about 225 million kilometers (140 million miles) away from Earth. But since both planets follow elliptical orbits, the distance can range from as close as 54.6 million kilometers (33.9 million miles) during opposition to as far as 401 million kilometers (249 million miles) at conjunction.
Now, let’s convert these distances into light years. At its closest approach, Mars is about 0.0000000588 light years from Earth. And at its farthest, it’s roughly 0.00000043 light years away. As you can see, these numbers are incredibly small when expressed in light years. That’s why we typically use other units for intra-solar system measurements.
The Importance of Orbital Positions
The distance between Earth and Mars changes constantly because both planets are constantly moving. When Earth and Mars are on opposite sides of the Sun, they’re at their farthest points from each other. This is called superior conjunction. On the flip side, when the two planets align on the same side of the Sun, Mars makes its closest approach to Earth. This event is known as opposition and happens roughly every 26 months.
During opposition, Mars appears brighter and larger in the night sky, making it a great time for stargazers to observe the red planet. It’s also the perfect opportunity for space agencies to launch missions to Mars, as the shorter distance reduces travel time and fuel consumption.
Understanding Astronomical Units (AU)
Before we dive deeper into the math, let’s talk about another important unit of measurement: the astronomical unit (AU). One AU is the average distance between Earth and the Sun, which is about 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles). Using AUs makes it easier to compare distances within our solar system.
At its closest, Mars is about 0.38 AU from Earth. At its farthest, the distance increases to around 2.65 AU. These numbers give us a clearer picture of the dynamic relationship between the two planets. Plus, they’re way easier to wrap your head around than trillions of kilometers or light years!
Why Astronomers Love AUs
AUs are like the Goldilocks unit of measurement for our solar system—not too big, not too small, just right. They allow astronomers to express distances in a manageable way while still conveying the immense scale of space. For example, Jupiter is about 5.2 AU from the Sun, while Neptune is a whopping 30 AU away. These numbers are much easier to comprehend than the equivalent distances in kilometers or miles.
When it comes to Earth and Mars, AUs provide a simple and effective way to describe their ever-changing separation. So, the next time someone asks you how far Mars is from Earth, you can confidently reply with the appropriate AU value!
Calculating the Distance Between Earth and Mars
Alright, let’s get our calculators out and crunch some numbers. To calculate the distance between Earth and Mars, we need to consider their positions in relation to the Sun. Both planets orbit the Sun in elliptical paths, so the distance between them is constantly changing.
- At closest approach (opposition): ~54.6 million km (~33.9 million miles)
- Average distance: ~225 million km (~140 million miles)
- At farthest distance (conjunction): ~401 million km (~249 million miles)
Converting these distances into light years gives us:
- Closest approach: ~0.0000000588 light years
- Average distance: ~0.000000237 light years
- Farthest distance: ~0.00000043 light years
As you can see, these numbers are incredibly small when expressed in light years. That’s why astronomers usually stick to kilometers, miles, or AUs when discussing distances within our solar system.
The Role of Kepler’s Laws
Kepler’s laws of planetary motion play a crucial role in calculating the distance between Earth and Mars. These laws describe how planets orbit the Sun in elliptical paths and how their speeds vary depending on their proximity to the Sun. By applying Kepler’s laws, astronomers can accurately predict the positions of Earth and Mars at any given time.
This precise knowledge is essential for planning space missions, such as NASA’s Mars rovers and orbiters. It ensures that spacecraft arrive at their destinations safely and efficiently, even when traveling millions of kilometers through the void of space.
How Long Does It Take to Travel from Earth to Mars?
Now that we know the distance between Earth and Mars, let’s talk about travel time. How long does it take to get from one planet to the other? The answer depends on several factors, including the type of spacecraft, its speed, and the alignment of the planets.
On average, a trip to Mars takes about 6-9 months. For example, NASA’s Perseverance rover took 203 days (about 6.7 months) to reach the red planet. During this time, the spacecraft travels along a curved trajectory called a Hohmann transfer orbit, which minimizes fuel consumption and travel time.
Challenges of Space Travel
Traveling to Mars isn’t as simple as hopping on a spaceship and pressing the “go” button. There are numerous challenges to overcome, including radiation exposure, life support systems, and navigation. Astronauts must also contend with the psychological effects of long-duration space travel, such as isolation and confinement.
Despite these challenges, humanity continues to push the boundaries of space exploration. With advancements in technology and increasing interest in Mars colonization, the dream of sending humans to the red planet is closer than ever before.
Why Is Mars So Fascinating?
Mars has captured the imagination of scientists, explorers, and dreamers for centuries. Its reddish hue, polar ice caps, and evidence of ancient rivers make it one of the most intriguing planets in our solar system. But what makes Mars so special?
For starters, it’s the most Earth-like planet we know of. Both planets have similar day lengths, seasons, and weather patterns. Mars also has a thin atmosphere composed mostly of carbon dioxide, with traces of nitrogen and argon. These similarities make it a prime candidate for future human exploration and colonization.
Exploring Mars’ Mysteries
Over the years, numerous missions have been sent to Mars to uncover its secrets. From the Viking landers in the 1970s to the Curiosity and Perseverance rovers today, each mission has added to our understanding of the red planet. Scientists have discovered evidence of liquid water, ancient river valleys, and even the possibility of microbial life.
These discoveries have fueled speculation about the potential for life on Mars, both past and present. While no definitive proof has been found yet, the search continues. Who knows what future missions might uncover?
What Does the Future Hold for Mars Exploration?
The future of Mars exploration looks bright. With plans for crewed missions and even colonization on the horizon, the red planet is set to become a major focus of space exploration in the coming decades. But what does this mean for humanity?
First and foremost, it represents a giant leap forward in our quest to understand the universe. By studying Mars, we can learn more about the formation and evolution of planets, the potential for life beyond Earth, and the limits of human endurance in space. It also opens up new possibilities for resource utilization, such as mining water and minerals from the Martian surface.
The Role of Private Companies
In addition to government space agencies like NASA and ESA, private companies like SpaceX are playing a crucial role in Mars exploration. SpaceX’s Starship spacecraft is designed to carry humans and cargo to Mars, paving the way for future colonization efforts. With ambitious goals like establishing a self-sustaining city on Mars, the possibilities seem endless.
Of course, there are still many challenges to overcome, including technological, financial, and ethical considerations. But with the combined efforts of governments, private companies, and scientists around the world, the dream of reaching Mars is becoming a reality.
Conclusion: The Final Frontier
And there you have it, folks! We’ve journeyed through the vastness of space to uncover the answer to the question: how many light years is Earth from Mars. While the distance may seem insignificant when expressed in light years, it’s still a mind-boggling reminder of just how far apart these two planets are.
From understanding light years and astronomical units to exploring the challenges of space travel and the mysteries of Mars itself, we’ve covered a lot of ground. But the journey doesn’t end here. As humanity continues to push the boundaries of exploration, the possibilities for discovery are endless.
So, what’s next? Will we find evidence of life on Mars? Will humans ever set foot on the red planet? Only time will tell. In the meantime, keep looking up and dreaming big. Who knows—maybe one day you’ll be part of the next great chapter in space exploration!
Feel free to leave your thoughts in the comments below or share this article with your fellow space enthusiasts. And don’t forget to check out our other articles for more fascinating insights into the universe. Until next time, keep reaching for the stars!
Table of Contents
- How Many Light Years is Earth from Mars? A Fascinating Journey Through Space
- What Exactly Are Light Years?
- Why Do We Use Light Years?
- How Far is Mars from Earth?
- The Importance of Orbital Positions
- Understanding Astronomical Units (AU)
- Why Astronomers Love AUs
- Calcul
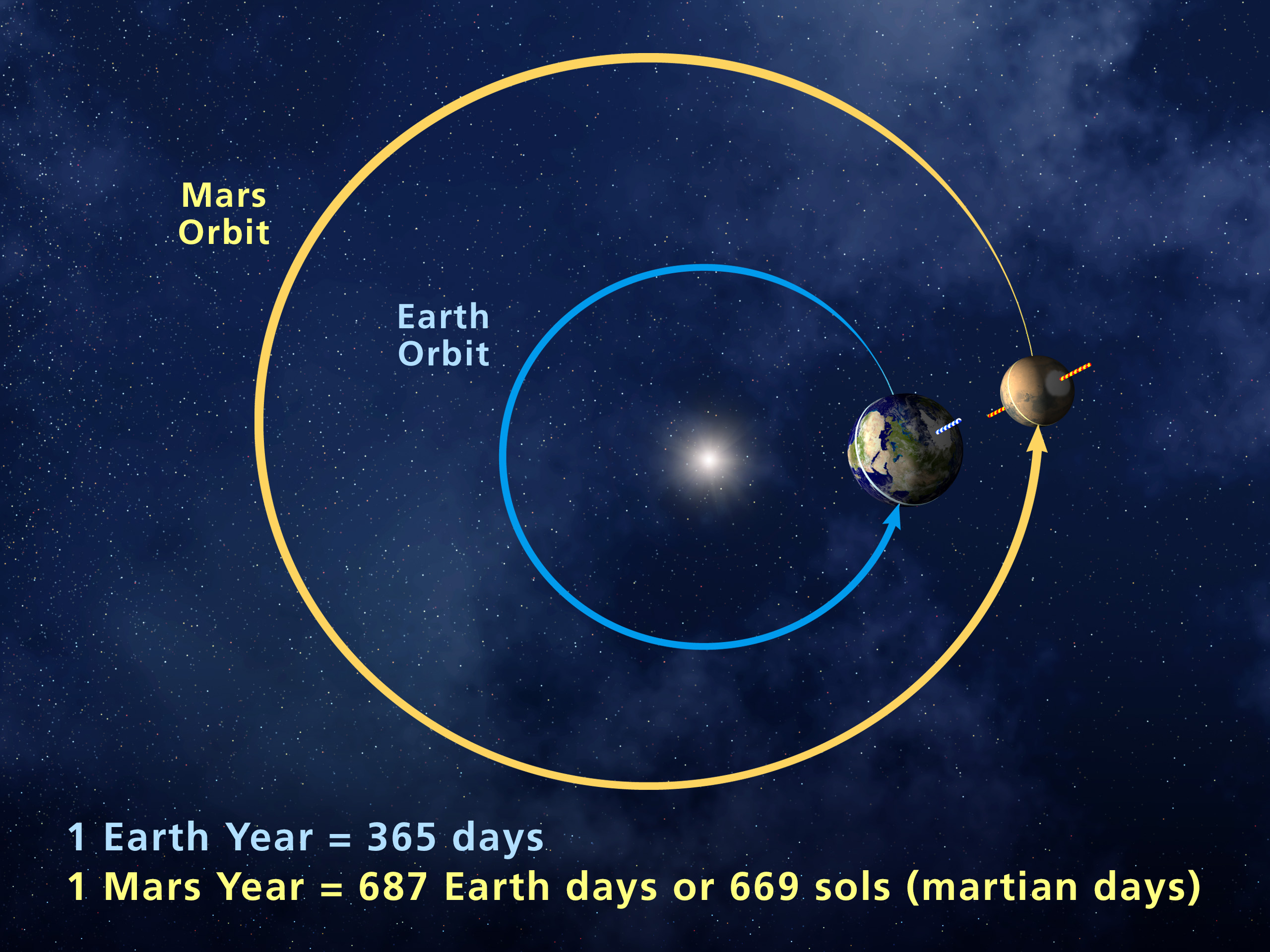
Martian Year Mars Exploration Program
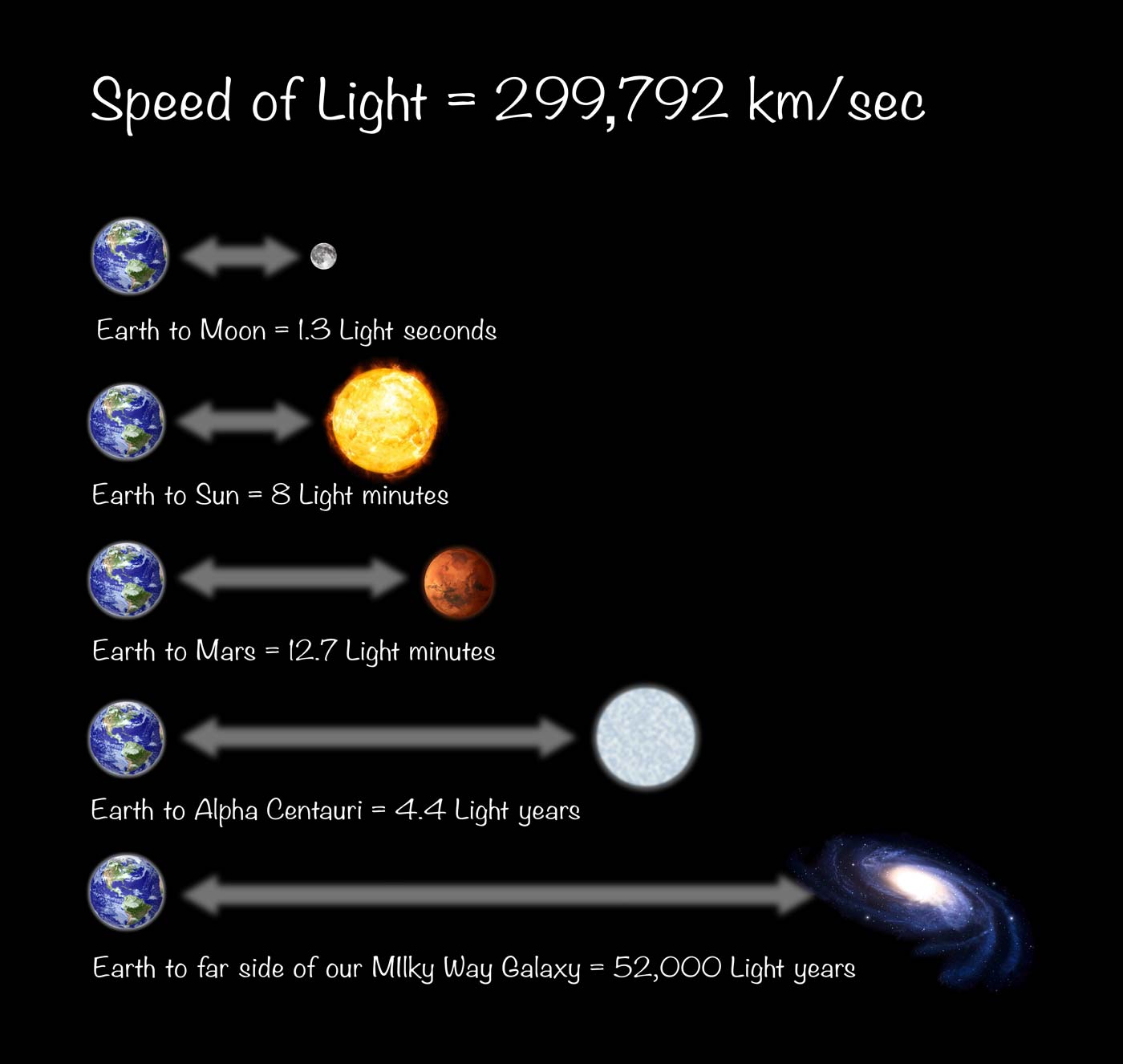
How long is a lightyear?

Mars Close Approach Mars in our Night Sky NASA’s Mars Exploration